Leaderboard
Popular Content
Showing content with the highest reputation on 02/07/2021 in all areas
-
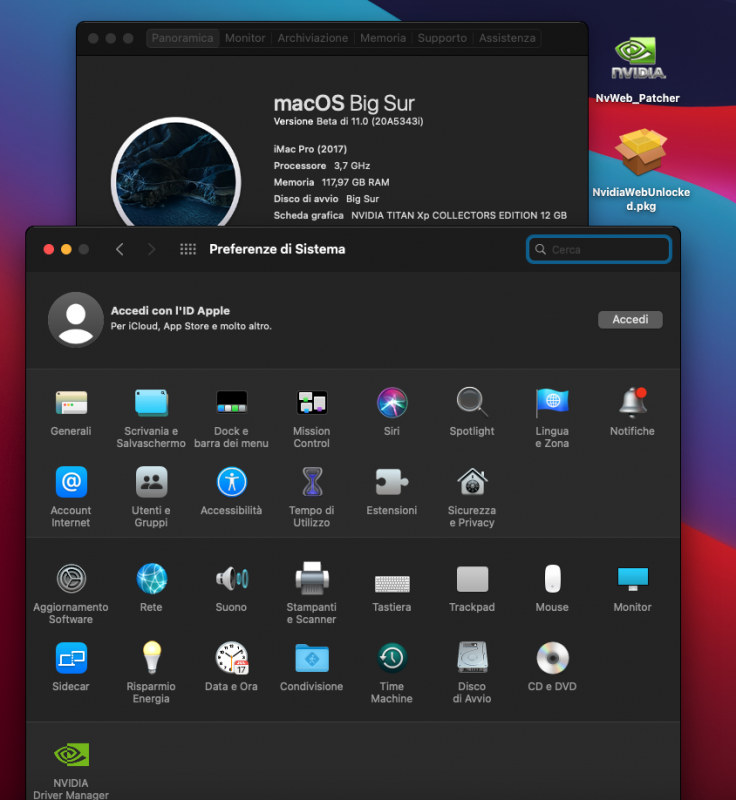
Quando il tuo Mac si “sbaglia”, viene spesso chiamato "crash". Questo è un termine breve, succinto, ma non molto utile a capire cosa è andato storto e come risolverlo. Comprendendo cosa è successo e cosa è stato esattamente quel "crash", otteniamo importanti indizi su cosa fare dopo. Uscita imprevista macOS ha aree protette, incluso il kernel stesso, che le app non dovrebbero essere in grado di influenzare. Ogni app viene eseguita in uno spazio separato, separato da altre app e dallo spazio di sistema protetto. Quindi il tipo più comune di "crash" dovrebbe essere un'app che morde la polvere quando ha fatto qualcosa di sbagliato. Di solito l'app si chiude improvvisamente, per questo viene spesso definita chiusura imprevista. Le uscite impreviste possono verificarsi per molti motivi, ma i più frequenti sono i bug nell'app. Se un'app si chiude ripetutamente in modo imprevisto quando provi a fare la stessa operazione, allora puoi essere abbastanza sicuro che si tratti di un bug in quell'app e dovresti segnalarlo agli sviluppatori dell'app. Naturalmente questo non è necessariamente una questione di colpa: molti di questi bug si verificano quando l'app si aspetta che macOS faccia qualcosa in un modo, e non è così. È quindi probabile che ci sia un periodo in cui gli sviluppatori dell'app danno la colpa a Apple, Apple dice poco e alla fine il problema viene risolto tranquillamente. Quando un'app si chiude inaspettatamente, macOS e tutte le altre app in esecuzione non devono essere interessate, ma a volte l'app, quando sta per uscire, lascia alcuni danni a macOS, ai file archiviati o altrove. Quindi, anche se dovresti essere sicuro di continuare a lavorare e riaprire l'app che si è chiusa, fai attenzione a eventuali segni di comportamenti strani che indicano danni residui. Il riavvio del Mac normalmente lo cancella. Esistono anche diversi motivi per cui macOS ha forzato la chiusura improvvisa della tua app. Se ciò accade quando l'app tenta di avviarsi, ad esempio, potrebbe essere perché si è verificato un errore di firma, ha tentato di accedere alle risorse protette dalla privacy a cui non aveva diritto o un problema con il codice oi file dell'app . Sfortunatamente, nella maggior parte dei casi, sia che si sia chiuso da solo, sia che sia stato forzato da macOS, tutto ciò che vedrai sarà un rapporto sugli arresti anomali, che potrebbe invitarti a riaprire l'app o a inviarlo ad Apple. La lettura dei rapporti sugli arresti anomali è un'attività piuttosto specializzata e normalmente necessita di informazioni dettagliate sul funzionamento di macOS e dell'app che si è chiusa. Se hai la possibilità di inviare il rapporto ad Apple o allo sviluppatore, ti preghiamo di farlo, poiché ciò potrebbe significare che il suo sviluppatore ha la possibilità di vederlo. Se vuoi capire i rapporti sugli arresti anomali, questa vecchia Nota tecnica li spiega e c'è un'intera sessione del WWDC 2018 dedicata all'argomento. Spinning beachball, o hang Più comuni delle uscite inaspettate sono gli “spinning beachball” (palloni da spiaggia che girano). Queste sono occasioni in cui un'app riscontra un problema e visualizza il puntatore come un beachball rotante per indicare che ci sta lavorando. Ciò potrebbe essere dovuto al fatto che hai chiesto all'app di intraprendere qualcosa di enorme: la maggior parte delle app mira a inserire attività di lunga durata in un processo in background e mostrare uno spinner o una barra di avanzamento occupati, ma ciò non è sempre possibile. Finché il pallone da spiaggia non viene visualizzato per troppo tempo, dovresti lasciare che l'app si risolva da sola. I beachball che girano non sono di per sé un'indicazione affidabile che un'app è in difficoltà: il loro significato è semplicemente che l'app in primo piano è troppo impegnata nell'elaborazione per interagire con l'utente al momento. In molte circostanze, questo è abbastanza benigno e l'app è semplicemente impegnata a fare quello che volevi. A volte un'app sembra incapace di riprendersi dal beachball re si blocca, non risponde, consuma i cicli della CPU e non arriva da nessuna parte. Dovresti essere in grado di forzare la chiusura dell'app, quindi puoi riaprirla e provare un approccio diverso. Per farlo, premi contemporaneamente Comando-Opzione + Esc per visualizzare la finestra di dialogo Uscita forzata. Seleziona l'app che si è bloccata, che di solito è contrassegnata in rosso segno che non risponde, quindi fai clic sul pulsante Uscita forzata. L'app verrà quindi chiusa e potrai riavviarla quando desideri e utilizzarla. Questo dovrebbe ripulire tutto correttamente dopo aver forzato la chiusura dell'app, ma come per le chiusure impreviste, a volte lascia macOS e altre app in una situazione instabile, che richiede un riavvio. Quando forzi la chiusura di un'app e, talvolta, in altre occasioni, macOS potrebbe generare automaticamente un rapporto "spindump"; genera anche rapporti "microstackshot" in caso di problemi di prestazioni. Sfortunatamente, interpretarli è davvero possibile solo se capisci come funziona l'app e cosa stava facendo in quel momento. I beachball rotanti ricorrenti in diverse app e il Finder sono una buona indicazione di problemi più generali con macOS piuttosto che con quelle app. Questi si verificano più comunemente quando hai appena aggiornato o aggiornato macOS e suggeriscono un aggiornamento non riuscito o un grave conflitto interno, forse con qualche prodotto di terze parti incompatibile. Una possibile soluzione è avviare in modalità provvisoria (con il tasto Maiusc tenuto premuto), lasciare il Mac per un minuto o due, quindi riavviare in modalità normale. Se ciò non risolve il problema, prova a scaricare e installare l'ultimo aggiornamento Combo o a reinstallare quella versione di macOS, magari in modalità di ripristino. Le estensioni di terze parti e altri software di livello inferiore sono disabilitati in modalità provvisoria, quindi potrresti scoprire che i beachball scompaiono in quella modalità. Tuttavia, anche molte estensioni Apple sono disabilitate e potresti non essere in grado di eseguire molte delle tue app. Kernel panic Le prime versioni di macOS spesso non proteggevano abbastanza bene il kernel e altre parti centrali del sistema e un bug pernicioso in un'app poteva far crollare l'intero sistema. È ora più probabile che ciò si verifichi a seguito di un errore hardware, come un problema di memoria o un guasto improvviso di un disco. Nella forma classica (OS X 10.7 e versioni precedenti), l'intero schermo del Mac diventa grigio e un messaggio multilingue ti informa che macOS ha riscontrato un errore e deve essere riavviato: questo è un kernel panic. Da OS X 10.8 in poi, questo comportamento è cambiato e potresti non essere nemmeno informato del kernel panic. Invece, il tuo Mac potrebbe bloccarsi per un minuto circa, quindi riavviarsi spontaneamente o semplicemente spegnersi del tutto. A meno che tu non gli abbia detto di riavviare o spegnere, questo può essere solo il risultato di un kernel panic. Se il tuo Mac ha un kernel panic, deve riavviare e caricare macOS da zero: il kernel ha subito così tanti danni che non può ripristinarsi in nessun altro modo. Puoi saperne di più su come riconoscere e gestire un panico del kernel qui. Freeze Quando il kernel di macOS e le parti centrali del sistema collassano completamente, potrebbero non essere in grado di continuare abbastanza a lungo da avvisarti con un kernel panic, né da riavviare prontamente. Invece, il tuo Mac si ferma semplicemente come un morto nell'acqua: l'orologio si ferma, non puoi navigare tra le finestre, anzi normalmente non puoi nemmeno muovere il puntatore. Un sintomo interessante che potrebbe avvisarti di un tale blocco è che un Apple Magic TrackPad 2, che è gestito dal software, perde la capacità di fare clic e si sente "morto". Se incappi in un blocco, lascia stare il Mac per un minuto o due, poiché è probabile che si riavvii automaticamente. In caso contrario, è necessario premere e tenere premuto il pulsante di accensione fino a quando non lo si è forzato a spegnersi, attendere alcuni secondi, quindi riavviarlo. Non scollegare o spegnere mai l'alimentazione di rete, tranne in caso di grave emergenza, poiché ciò comporta un alto rischio di causare danni permanenti al tuo Mac, sia al suo software che possibilmente al suo hardware. Come il kernel panic, dovresti vedere un blocco solo se hai un problema hardware. Tuttavia, le versioni successive di El Capitan (10.11.4 e successive) sono note per causare ripetuti blocchi sporadici su alcuni modelli di Mac, inclusi alcuni iMac e MacBook Pro. Questo è stato risolto correttamente solo con il nuovo kernel fornito in macOS Sierra, che per la maggior parte degli utenti è molto più robusto. Sono stati segnalati blocchi anche su alcuni modelli con determinate versioni di firmware. Problemi associati a eventi specifici L'arresto anomalo che si verifica durante l'avvio può essere particolarmente difficile da individuare, soprattutto se impedisce al tuo Mac di avviarsi completamente. Gravi problemi che lasciano il tuo Mac con uno schermo colorato uniforme, in genere nero o blu, di solito indicano un guasto hardware, come una scheda grafica difettosa. I problemi minori vengono spesso risolti riavviando in modalità provvisoria, con il tasto Maiusc tenuto premuto; questo disabilita la maggior parte del software di terze parti e può consentire di capire cosa si sta verificando e affrontarlo. Un altro momento critico in cui si verificano problemi è al “Wake from sleep” (risveglio dal sonno). Ciò normalmente richiede che macOS riattivi l'hardware e potrebbe essere necessario caricare driver e altro software di basso livello. Può provocare uno qualsiasi dei suddetti tipi di incidente. È più insolito andare in crash quando si va in Sleep, ma questo è un altro indicatore utile che può aiutare a restringere la causa. Gli indizi più importanti di tutti? La maggior parte degli eventi di cui sopra vengono registrati con informazioni dettagliate nei log del tuo Mac. In El Capitan e versioni precedenti, puoi sfogliare quelli che utilizzano Console, ma purtroppo Sierra ha introdotto un nuovo sistema di registrazione e Console ora ha un valore molto limitato. Se utilizzi Sierra o versioni successive, dovrai usare applicazioni di terze parti, ma questo è un’altro discorso. (Cit. EclecticLight)3 points
-
Quando si fanno alcune operazioni nel sistema, per completare correttamente è necessario aggiornare la cache dei DNS; i Domain Name System sono delle tabelle di associazione di dati per conversione degli indirizzi web, altrimenti raggiungibili solo tramite un IP numerico. Le operazioni più comuni dove questo necessita, usuali e frequenti sui server e molto meno sui sistemi di utenze personali, sono: - Cambiamenti nel file hosts - variazione dei DNS nell’omonimo pannello di Preferenze Network - Lentezza nel risolvere l’indirizzo web in navigazione Svuotare la cache DNS in Tiger OS X 10.4: lookupd -flushcache Svuotare la cache DNS in Leopard OS X 10.5 e Snow Leopard OS X 10.6: sudo dscacheutil -flushcache Svuotare la cache DNS in Lion OS X 10.7 e Mountain Lion OS X 10.8 sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder Svuotare la cache DNS in Mavericks OS X 10.9: dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder Svuotare la cache DNS in Yosemite OS X 10.10: sudo discoveryutil mdnsflushcache;sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches Svuotare la cache DNS in El Capitan OS X 10.11, MacOS 10.12 Sierra: sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder Svuotare la cache DNS in MacOS 10.13 High Sierra, MacOS 10.14 Mojave, MacOS 10.15 Catalina: sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder Svuotare la cache DNS in MacOS 11 Big Sur: sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder (Cit.Faxus)3 points
-
Per ora non ci sono opzioni imminenti se non Vega o una serie 5xxx come modelli superiori alla tua attuale2 points
-
se guardi la mia firma..forse capisci che anche io ho pensato lo stesso... ed ho ripiegato su una rx 580 8 Gb poi se sarà il supporto disponibile..si prenderà di nuovo un GPU della serie RX6xxx2 points
-
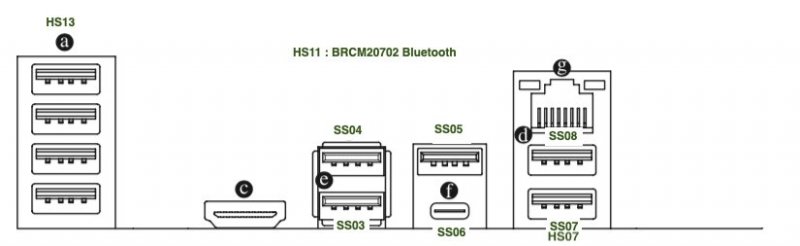
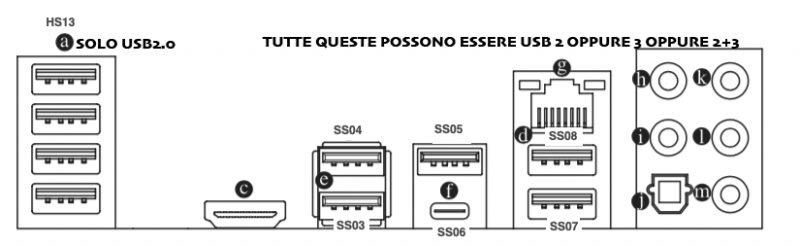
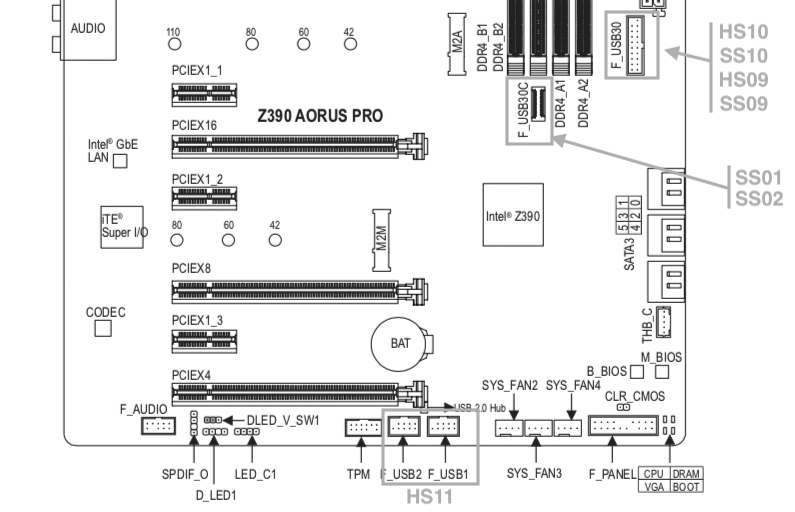
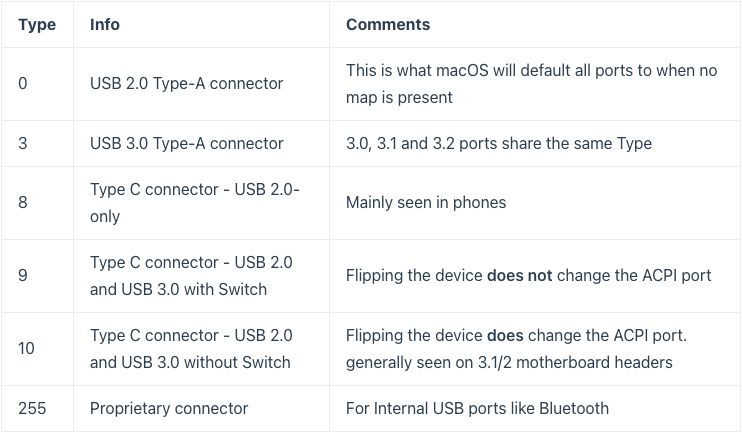
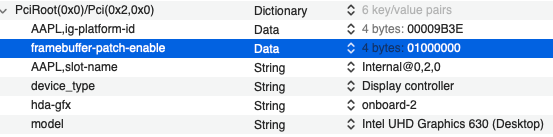
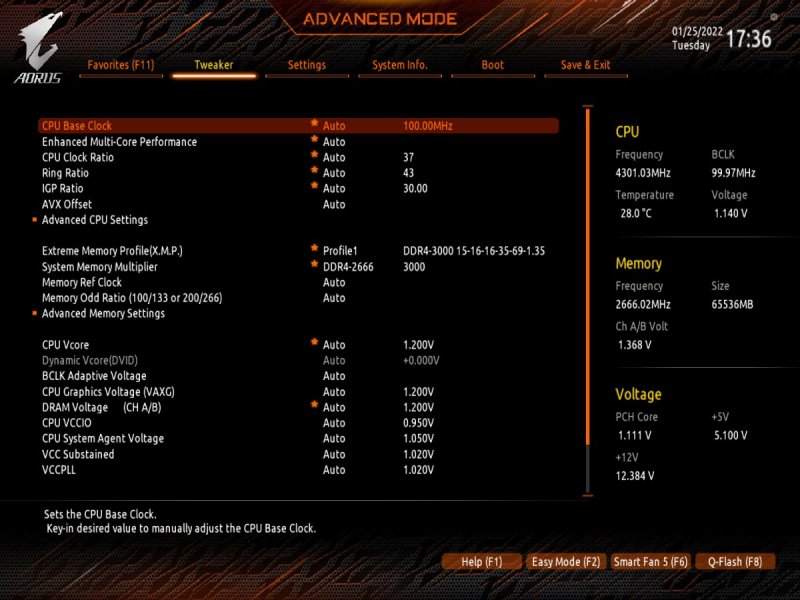
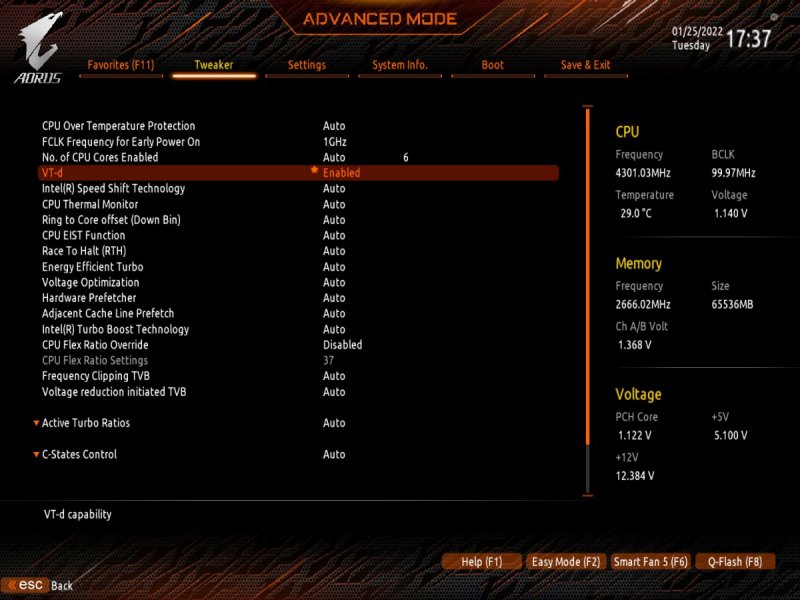
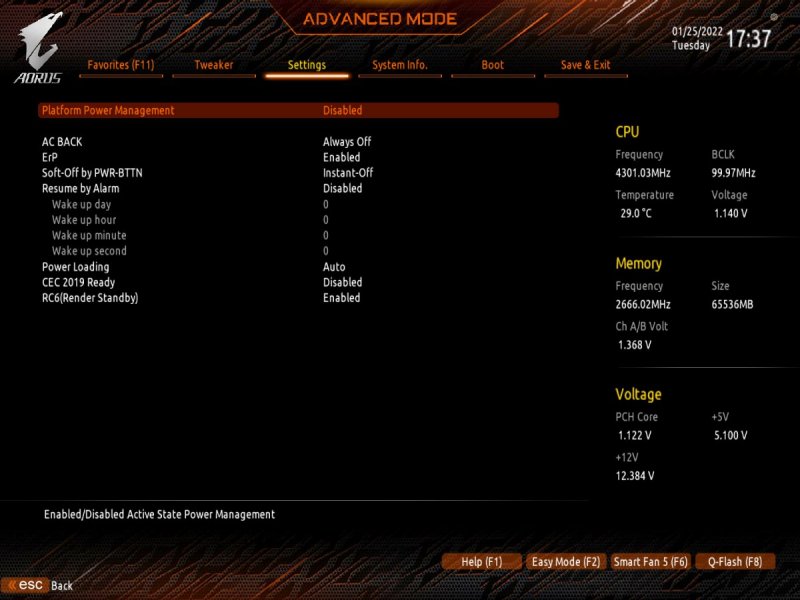
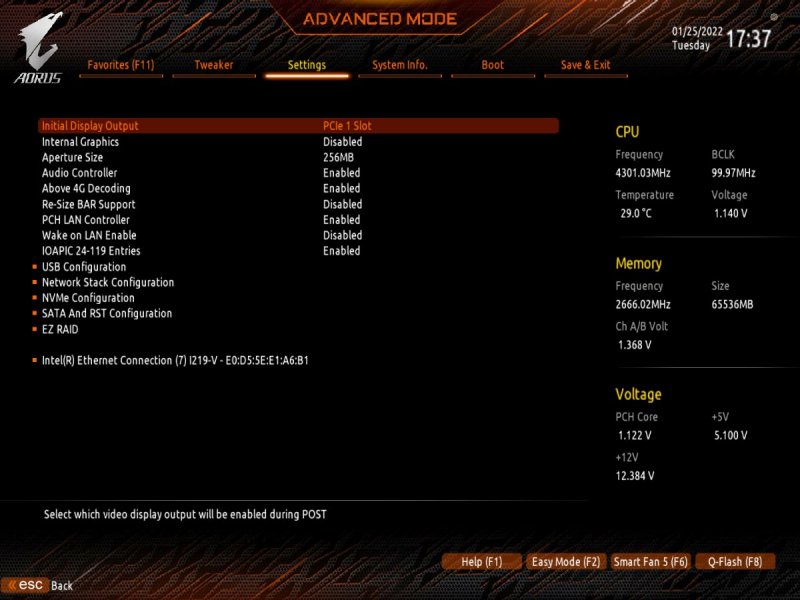
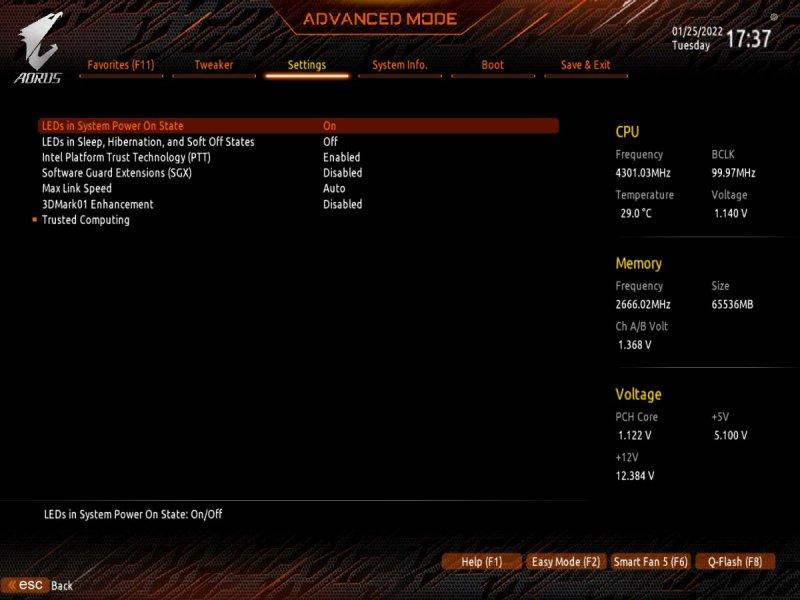
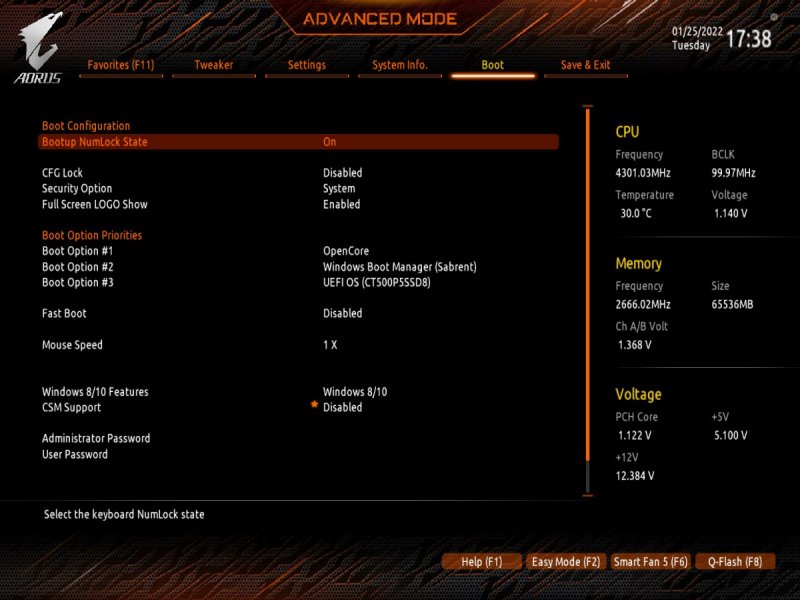
Buongiorno a tutti, posto qui le mie riflessioni e la mia mini-guida all’installazione di BigSur / Monterey su scheda madre Z390 Gigabyte Aorus Pro (guida compatibile anche con Aorus PRO WIFI , previa disabilitazione wifi non compatibile con OSX in quanto chipset intel) Cominciamo…. In questa guida, sono stati utilizzati i seguenti componenti e soprattutto nessuno è stato maltrattato! : Mainboard: Gigabyte Aorus Pro rev1,0 chipset z390 bios f12l CPU: Intel i5 9600k RAM: Ballistix Sport LT (4x16gb) Video: AMD Sapphire RX580 Nitro+ CPU Cooler: iTek Liqui v2 240 (modificato) NVMe: CRUCIAL P5 500gb Case: Deepcool Matrex 70 WiFi/BT: Abwb 802.11AC BT4.0 chipset BCM943602CS pci-e Vari SSD e HDD che però a noi non interessano... Hardware: EFI OpenCore 0.8.0 con DevirtualiseMmio OFF (consigliato profilo bios in guida) COSA FUNZIONA: • Porta Ethernet • Audio • WiFi (con il modulo utilizzato in questa guida OOB installato nella PCI-E più in basso) • SSD Trim • USB 3.0 , USB 2.0 e USB-C (USB-C interna DISABILITATA con mappatura) • AirDrop (con il modulo utilizzato in questa guida OOB installato nella PCI-E più in basso) • iCloud • Accelerazione Hardware h264/HEVC • iMessages • Facetime • Sleep e Wake • Sleep e Spegnimento tramite pulsante Power • Handoff • Continuity • Netflix 1080p/4k Safari (funzionante SOLO su efi iMacPro1,1 e MacPro7,1) • NVRAM • AppleTV 1080p/4k (funzionante SOLO su efi iMacPro1,1 e MacPro7,1) COSA NON FUNZIONA: • Sidecar (funzionante SOLO su efi iMac19,1) • Null’altro (ditemi voi in caso!) OCCORRENTE: • Chiavetta USB installazione Big Sur / Monterey (BETA) con EFI ottimizzata (in allegato) • Una Aorus PRO Z390 con bios f12 • Una RX580/590 • Un monitor xD • Un mouse e una tastiera LoL Prepariamo la chiavetta di installazione: Per fare questo, o emulate osx su macchina virtuale da Windows o usate un vero Mac/Hack. In questo Forum , è presente la guida alla creazione Vanilla (no Vanilla Ice, gli anni 80 son finiti ahimè)… seguite quella! …..Dopo questa bruttissima battuta, alla fine della creazione della vostra chiavetta di installazione, dovrete copiare la cartella EFI allegata alla guida. Non preoccupatevi, la cartella che scaricherete, non è nient’altro che una EFI di OpenCore opportunamente modificata per la nostra scheda madre e per la nostra RX580, completa di SSDT e di mappatura USB effettuata come riportato in foto allegata... IMPOSTAZIONI BIOS: (impostazioni basate su versione f12k o successive – meglio aggiornare almeno a f12 - bios f12 allegato al fondo della discussione) Per prima cosa, una volta assemblato il tutto, facciamo partire la macchina. Entriamo nel BIOS (con il tasto CANC) Carichiamo le impostazioni di default, riavviamo e rientriamo nuovamente nel BIOS A questo punto, andiamo a cliccare su “Advanced Mode” per attivare l’interfaccia completa. Inseriamo le seguenti impostazioni, lasciando TUTTO il resto di default: • Boot -> Boot -> CFG Lock -> Disabled • Boot -> Windows 8/10 Features -> Windows 8/10 (Attenzione, questo deve essere su Other SOLO se usate sistemi Linux con bootloader grub proprietario. Se usate OpenCore, DEVE essere Windows 8/10) • Boot -> CSM Support -> Disabled • Tweaker -> Extreme Memory Profile (X.M.P.) -> Profile1 • Tweaker -> System Memory Multiplier -> DDR4-2666 (solo se avete memorie con profilo superiore ai 2666 ...poi vi spiego****) • Tweaker -> Advanced CPU Settings -> VT-d -> Disabled • Settings -> IO Ports -> USB Configuration -> Legacy USB Support -> Enabled • Settings -> IO Ports -> USB Configuration -> XHCI Hand-off -> Enabled • Settings -> IO Ports -> USB Configuration -> USB Mass Storage Driver Support -> Enabled • Settings -> IO Ports -> USB Configuration -> Port 60/64 Emulation -> Disabled • Settings -> IO Ports -> Initial Display Output -> PCIe 1 Slot • Settings -> IO Ports -> Internal Graphics -> Disabled (Per smbios iMacPro1,1 ;;; invece impostate su "Enabled" e con memoria settata a 64MB per smbios iMac19,1) • Settings -> IO Ports -> DVMT -> MAX • Settings -> IO Ports -> Aperture Size -> 256MB • Settings -> IO Ports -> Above 4G Decoding -> Enabled • Settings -> IO Ports -> Resize BAR Support -> Disabled (Mettere su "Auto" se desiderate utilizzare le funzionalità Resizable Bar con schede video serie 5xxx 6xxx - con schede Polaris è irrilevante e non serve a nulla) • Settings -> Miscellaneous -> Intel Platform Trust Tecnology (PTT) -> Enabled • Settings -> Miscellaneous -> Software Guard Extensions (SGX) -> Disabled • Settings -> Miscellaneous -> Trusted Computing -> Disabled (Enabled se vogliamo utilizzare Windows 11) • Settings -> Platform Power -> Platform Power Management -> Disabled • Settings -> Platform Power -> ErP -> Enabled • Settings -> Platform Power -> RC6(Render Standby) -> Enabled • Save & Exit → Save & Exit Setup Avendo io il bios settato in lingua inglese, ho riportato tutti i menu scritti in inglese! Ma comunque vi posto le foto per far rendere l’idea di cosa impostare! Bios: Non resta che partire con l’installazione di OSX vera e propria! Avviate l’installazione normalmente seguendo i canonici passi. L’unico accorgimento è, una volta installato il tutto, utilizzare il vostro editor plist preferito , (possibilmente NON textedit) e modificare i dati "sensibili" (seriale , mlb , smuuid , mac address**). iMac19,1 è il più "consono" per i processori CoffeeLake e la nostra scheda madre ma per determinate situazioni, sono meglio iMacPro1,1 e MacPro7,1 (io uso quest'ultimo). In alternativa, se non si possiede una scheda video PCIe, si usa iMac19,1 UHD630 che prevede l'utilizzo della scheda video integrata. **Nella sezione “PlatfotmInfo -> Generic” "ROM" , dovrete inserire il MAC Address della vostra scheda di rete con l’esclusione dei “ : “ esempio, Mac address: D0:81:7A:CF:13:B2, diventerà D0817ACF13B2 . Questa precauzione, farà funzionare senza problemi, dopo aver configurato un account apple, iMessage e FaceTime! Nelle EFI presenti in questa guida, potrete trovare il tema Aorus con HiDPI impostato di default per quanto riguarda la GUI di OpenCore. A questo punto, BUON HACK CON AORUS PRO Z390! 😄 PS Aggiornate tranquillamente alle nuove versioni di MacOS previo aggiornamento di OpenCore e Kext in caso (questa EFI è testata fino alla versione di MacOS Monterey 12.2 21d48)… Saluti! UHD630 (per conoscenza, e per capire le differenze): ATTENZIONE: Le efi che scaricate da qui, contengono la mappatura USB tramite KEXT e non più tramite patch ACPI Le porte sono attivate come segue: PORTE A FUNZIONE SINGOLA: HS11 HUB* INTERNO PER SCHEDA BLUETOOTH CONFIGURATO COME USB 2.0 (QUESTA PORTA CONTROLLA ANCHE LE USB2.0 FRONTALI) ""CODICE PORTA 255"" HS12 GESTORE PORTE CHIP USB DA NON CANCELLARE ASSOLUTAMENTE ""CODICE PORTA 0"" HS13 HUB* POSTERIORE 4 PORTE USB 2.0 ""CODICE PORTA 0"" SS04 USB 3.0 POSTERIORE ""CODICE PORTA 3"" SS09 USB 3.0 FRONTALE ""CODICE PORTA 3"" HS10 USB 2.0 FRONTALE ""CODICE PORTA 0"" PORTE A FUNZIONE DOPPIA USB2.0 USB3.0: HS07/SS07 USB 2.0 / USB 3.0 ""CODICE PORTA 0 / 3"" HS08/SS08 USB 2.0 / USB 3.0 ""CODICE PORTA 0 / 3"" PORTE A FUNZIONE DOPPIA USB3.0 USB3.1: SS03 USB 3.0 USB 3.1 ""CODICE PORTA 3"" SS05 USB 3.0 USB 3.1 ""CODICE PORTA 3"" PORTE A FUNZIONE TRIPLA: HS06/SS06 USB TYPE-C 2.0 / USB TYPE-C 3.0 / USB TYPE-C 3.1 CON AUTO SWITCH ""CODICE PORTA 10"" * ESSENDO UN HUB , VIENE CONTAT0 INDIPENDENTEMENTE DAL NUMERO DI CONNESSIONI PRESENTI, COME UNA PORTA SINGOLA PER IL LIMITE DI 15 TUTTE LE PORTE USB, FUNZIONANO AL MASSIMO DELLE LORO POSSIBILITA'. Modifica USB Kext (mappatura usb): CpuFriend Informazioni Utili: File Utili: Info per gli update: ATTENZIONE Per poter vedere gli aggiornamenti, da BigSur in avanti, il SIP va tenuto abilitato. Nelle EFI che scaricate da qui, è ABILITATO DI DEFAULT. **** questa accortezza, evita il fastidioso problema delle usb disconnesse dopo il wake e fa in modo che il sistema si risvegli dopo solo un clic del mouse e non dopo due.1 point
-
se anche quella è una porta fisica dove tu puoi collegare un dispositivo esterno allora deve essere 0x00 se fosse BT, come anche per esempio un lettore SD sul case quindi collegato a usb interna diretta sulla mobo, allora va interna 0xFF (255 in decimale)1 point
-
forse perché hai sbagliato qualcosa?! in _UPC devi sostituire Return (GUPC (One)) con --> Return (GENG (One, 0x00)) questo per le porte USB2 come definire le porte è spiegato nel txt e visto che come me, fare casini è un'attimo, ad ogni sostituzione, compila, così se hai sbagliato qualcosa, anche uno spazio, avrai un'errore e capisci subito dove hai cannato 😉1 point
-
Soddisfatto del binomio RX 460 in macOS + RTX 3070 in Winzozz. Tanto non gioco in macOS e per quello che faccio io la 460 è una gpu sufficiente fino a nuova disponibilità di gpu "potenti" 😉 Quanto al gaming in winzozz... un altro pianeta rispetto alla VII che avevo!1 point
-
No, al momento nessuno sa nulla si spera presto...ma potrebbe essere anche che non arriverà mai! Spostato in Big Sur discussioni generali...se ci sarà il supporto molto probabilmente sarà in Big Sur1 point
-
ciao avevi sritto in guide di riferimento visto che non ci sono molti dati sul notebook in questione.. io proverei ad entrare nel bios..leggi che tasto devi premere quando vedi la scritta lenovo... e magari a rimettere tutto a default1 point
-
1 point
-
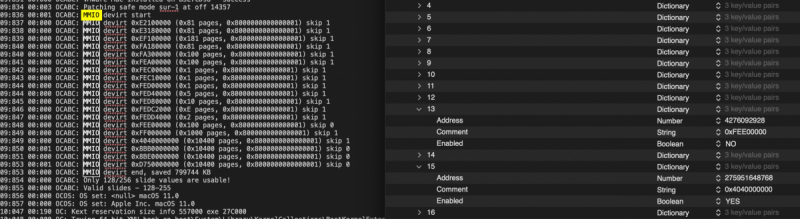
OK. in my case MMIO are the same also with both options on.. system in bios configuration does not boot if both are enabled1 point
-
1 point
-
11.2 Release Candidate is on no Big navi2 support 😞 OSX does not work if that feature is on on your BIOS for now!1 point
-
however it is a big improvment I am ashamed and a little embarrassed to tell you that I no longer have my EFI proxmox working 🙂 I have to research it, but when I got the Vega 64 I tried to do several restarts but I don't think I had the problem, I also seem to have written it As soon as I can try again1 point
-
@dtek our motherboard has 2 i211 intel ethernet they need of small5276 kext in other aquantia is an external card and it is seen by default in Bs it needs of a kexttopatch to work personally never used imessage or facetime on my hackintosh1 point
-
@meina222 I did in the past and I do not remember any particular problem I did with latest virtio drivers iso available, but to install I need in the start only of windows.iso downloaded from microsoft and a vm.conf created as usual1 point
-
hi @23d1welcome here glad to see your triple 1080ti GPU rig I think you will try macOS High Sierra to have a full GPU driver support In Proxmox should be more simple than bare metal because in bare metal trx40 and HighSierra have some additional problem to solve1 point
-
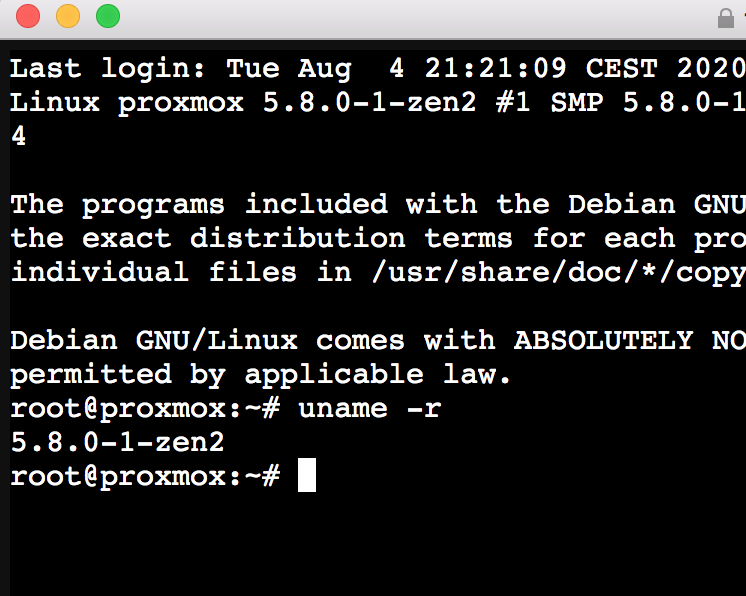
I have had to revert to old fabian 5.78.1 kernel for me this one is latest which works perfectly With 5.8.x I have an instable system. it reboots my VM in a random way I have associated this problem to my 2 10TB exsata disks or to my two 6tb data disks (not seen in osx because they are formatted in windows software raid) these disks some time appear after few minutes in desktop..and often with 5.8.x kernel produce a vm reboot with 5.78.1 this fact does not happen and system is perfect1 point
-
1 point
-
as info for all..it is possible to boot in bare metal or in Proxmox with the same bios settings Bad..very bad news..Our (mine) trx40 has not a native NVRAM For now I am not be able to activate my Nvidia Web drivers in High Sierra so I can't do a computation with GPU test CPU is the same Under load in CB20 I see 360 watt of power draw 🙂 Used AMD Per Gadget tools to monitor it this thread for Bare Metal discover or simply to talk about :91 point
-
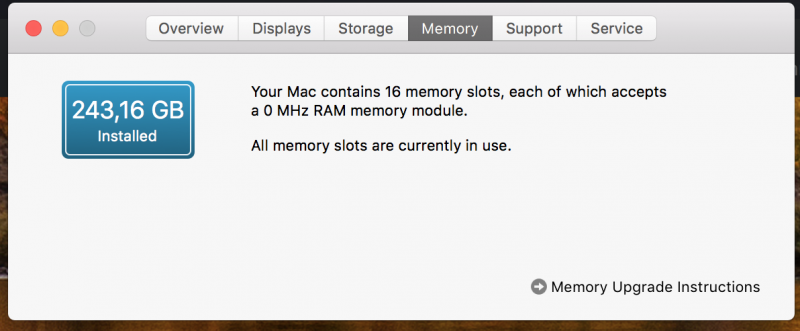
@iGPUcould you post a screenshot of about my Mac memory section? i would like to see how 32gb modules are seen in your rig i have bought four modules but there I see 8 slot full populated with 16 gb modules each also other users with 32gb modules type if possible thank you1 point
-
C [M] drivers/usb/usbip/stub_rx.o CC [M] net/sunrpc/auth_gss/gss_krb5_crypto.o AR drivers/net/wireless/atmel/built-in.a CC [M] drivers/net/wireless/atmel/atmel.o CC [M] drivers/usb/serial/garmin_gps.o CC [M] drivers/net/wireless/ath/ath6kl/bmi.o CC [M] drivers/net/wireless/atmel/atmel_pci.o CC [M] drivers/net/wireless/ath/ath9k/xmit.o CC [M] drivers/scsi/aic7xxx/aic7xxx_93cx6.o CC [M] drivers/net/wireless/atmel/atmel_cs.o CC [M] drivers/gpu/drm/nouveau/nvkm/subdev/clk/pllnv04.o CC [M] drivers/rtc/rtc-max8925.o CC [M] drivers/scsi/aic94xx/aic94xx_init.o CC [M] drivers/rtc/rtc-max8997.o CC [M] drivers/watchdog/retu_wdt.o CC [M] drivers/input/touchscreen/resistive-adc-touch.o CC [M] drivers/net/wireless/ath/carl9170/phy.o CC [M] drivers/scsi/aic7xxx/aic7770.o LD [M] dri is doing something1 point
-
root@proxmox:~# dpkg-architecture -bash: dpkg-architecture: command not found root@proxmox:~#1 point
-
root@proxmox:~/pve-edge-kernel# nano /etc/apt/sources.list root@proxmox:~/pve-edge-kernel# apt update Hit:1 http://security.debian.org/debian-security buster/updates InRelease Hit:2 http://download.proxmox.com/debian/pve buster InRelease Hit:3 http://ftp.debian.org/debian buster InRelease Get:4 http://ftp.debian.org/debian buster-updates InRelease [51.9 kB] Fetched 51.9 kB in 1s (61.2 kB/s) Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done 75 packages can be upgraded. Run 'apt list --upgradable' to see them. root@proxmox:~/pve-edge-kernel# then?1 point
-
root@proxmox:~# apt list dpkg-dev Listing... Done dpkg-dev/testing 1.20.5 all N: There is 1 additional version. Please use the '-a' switch to see it root@proxmox:~# apt install dpkg-dev Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: binutils binutils-common binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu cpp cpp-9 fakeroot gcc gcc-10-base gcc-9 gcc-9-base glusterfs-common libalgorithm-diff-perl libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl libalgorithm-merge-perl libanyevent-perl libapt-pkg-perl libapt-pkg6.0 libasan5 libatomic1 libauthen-pam-perl libbinutils libc-bin libc-dev-bin libc-l10n libc6 libcbor0 libcc1-0 libclone-perl libcommon-sense-perl libcrypt-openssl-bignum-perl libcrypt-openssl-random-perl libcrypt-openssl-rsa-perl libcrypt-ssleay-perl libcrypt1 libctf-nobfd0 libctf0 libdpkg-perl libfakeroot libfido2-1 libfile-fcntllock-perl libfilesys-df-perl libgcc-9-dev libgcc-s1 libgfapi0 libgfchangelog0 libgfrpc0 libgfxdr0 libglusterd0 libglusterfs0 libgomp1 libhtml-parser-perl libisl22 libitm1 libjson-xs-perl liblinux-inotify2-perl liblocale-gettext-perl liblsan0 libmpc3 libmpfr6 libnet-dbus-perl libnet-ssleay-perl libperl5.30 libquadmath0 libreadline8 librrds-perl libstdc++6 libtemplate-perl libterm-readline-gnu-perl libtext-charwidth-perl libtext-iconv-perl libtsan0 libubsan1 liburcu6 libuuid-perl libxml-libxml-perl libxml-parser-perl locales openssh-client openssh-server openssh-sftp-server perl perl-base perl-modules-5.30 runit-helper Suggested packages: binutils-doc cpp-doc gcc-9-locales debian-keyring gcc-multilib manpages-dev autoconf automake libtool flex bison gdb gcc-doc gcc-9-multilib gcc-9-doc libev-perl libevent-perl libio-async-perl libpoe-perl libtask-weaken-perl glibc-doc bzr libdata-dump-perl iwatch libtemplate-plugin-gd-perl libtemplate-plugin-xml-perl keychain libpam-ssh monkeysphere ssh-askpass molly-guard ufw perl-doc libtap-harness-archive-perl Recommended packages: build-essential libc6-dev | libc-dev libc6-dev libasync-interrupt-perl libev-perl | libevent-perl libguard-perl apt manpages-dev xauth The following packages will be REMOVED: libacl1-dev libattr1-dev libc6-dev libglusterfs-dev libpve-access-control libpve-cluster-api-perl libpve-guest-common-perl libpve-storage-perl libpve-u2f-server-perl librados2-perl proxmox-ve pve-cluster pve-container pve-firewall pve-ha-manager pve-manager qemu-server The following NEW packages will be installed: binutils binutils-common binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu cpp cpp-9 dpkg-dev fakeroot gcc gcc-10-base gcc-9 gcc-9-base libalgorithm-diff-perl libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl libalgorithm-merge-perl libapt-pkg6.0 libasan5 libatomic1 libbinutils libcbor0 libcc1-0 libcrypt1 libctf-nobfd0 libctf0 libdpkg-perl libfakeroot libfido2-1 libfile-fcntllock-perl libgcc-9-dev libgcc-s1 libglusterd0 libgomp1 libisl22 libitm1 liblsan0 libmpc3 libmpfr6 libperl5.30 libreadline8 libtsan0 libubsan1 perl-modules-5.30 runit-helper The following packages will be upgraded: glusterfs-common libanyevent-perl libapt-pkg-perl libauthen-pam-perl libc-bin libc-dev-bin libc-l10n libc6 libclone-perl libcommon-sense-perl libcrypt-openssl-bignum-perl libcrypt-openssl-random-perl libcrypt-openssl-rsa-perl libcrypt-ssleay-perl libfilesys-df-perl libgfapi0 libgfchangelog0 libgfrpc0 libgfxdr0 libglusterfs0 libhtml-parser-perl libjson-xs-perl liblinux-inotify2-perl liblocale-gettext-perl libnet-dbus-perl libnet-ssleay-perl libquadmath0 librrds-perl libstdc++6 libtemplate-perl libterm-readline-gnu-perl libtext-charwidth-perl libtext-iconv-perl liburcu6 libuuid-perl libxml-libxml-perl libxml-parser-perl locales openssh-client openssh-server openssh-sftp-server perl perl-base 43 upgraded, 42 newly installed, 17 to remove and 470 not upgraded. Need to get 22.3 MB/79.2 MB of archives. After this operation, 135 MB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y Get:1 http://http.us.debian.org/debian testing/main amd64 libgfxdr0 amd64 8.0-2 [2,761 kB] Get:2 http://http.us.debian.org/debian testing/main amd64 libglusterfs0 amd64 8.0-2 [3,027 kB] Get:3 http://http.us.debian.org/debian testing/main amd64 libgfrpc0 amd64 8.0-2 [2,788 kB] Get:4 http://http.us.debian.org/debian testing/main amd64 libgfapi0 amd64 8.0-2 [2,813 kB] Get:5 http://http.us.debian.org/debian testing/main amd64 libgfchangelog0 amd64 8.0-2 [2,768 kB] Get:6 http://http.us.debian.org/debian testing/main amd64 libglusterd0 amd64 8.0-2 [2,747 kB] Get:7 http://http.us.debian.org/debian testing/main amd64 liburcu6 amd64 0.12.1-1 [70.3 kB] Get:8 http://http.us.debian.org/debian testing/main amd64 glusterfs-common amd64 8.0-2 [5,358 kB] Fetched 22.3 MB in 50s (444 kB/s) W: (pve-apt-hook) !! WARNING !! W: (pve-apt-hook) You are attempting to remove the meta-package 'proxmox-ve'! W: (pve-apt-hook) W: (pve-apt-hook) If you really want to permanently remove 'proxmox-ve' from your system, run the following command W: (pve-apt-hook) touch '/please-remove-proxmox-ve' W: (pve-apt-hook) run apt purge proxmox-ve to remove the meta-package W: (pve-apt-hook) and repeat your apt invocation. W: (pve-apt-hook) W: (pve-apt-hook) If you are unsure why 'proxmox-ve' would be removed, please verify W: (pve-apt-hook) - your APT repository settings W: (pve-apt-hook) - that you are using 'apt full-upgrade' to upgrade your system E: Sub-process /usr/share/proxmox-ve/pve-apt-hook returned an error code (1) E: Failure running script /usr/share/proxmox-ve/pve-apt-hook root@proxmox:~# root@proxmox:~# dir gruppi.sh pve-edge-headers-5.7.8-1_5.7.8-1_amd64.deb pve-edge-kernel pve-edge-kernel-5.7.8-1-zen2_5.7.8-1_amd64.deb root@proxmox:~# cd pve-edge-kernel root@proxmox:~/pve-edge-kernel# make clean && make Using build type: zen2 make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory rm -rf *~ build *.prepared config-5.8.0.org rm -f *.deb *.changes *.buildinfo Using build type: zen2 make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory make: dpkg-architecture: No such file or directory rm -rf build/linux linux.prepared mkdir -p build cp -a submodules/linux build/linux cp -a debian-kernel/debian debian-kernel/debian.master build/linux/ cat build/linux/debian.master/config/config.common.ubuntu build/linux/debian.master/config//config.common. build/linux/debian.master/config//config.flavour.generic > config-5.8.0.org cat: build/linux/debian.master/config//config.common.: No such file or directory cat: build/linux/debian.master/config//config.flavour.generic: No such file or directory make: *** [Makefile:117: linux.prepared] Error 1 root@proxmox:~/pve-edge-kernel#1 point
-
hi @mclarenf1if you have 64 Gb of ram you have to put less in your vm config then if you want put your EFI without apple folder which are you using to boot ah also your cores number seems weird you have a 24+24 cpu so you can use 48 or you can use sockets=2 by the way some 3960x users said they can't pass in socket 1 and 48 their CPU and they have had to do different combination with cores and sockets number but..if you see apple logo..you are a step on 🙂1 point
-
Thank you @meina222 i will try to test high Sierra with Big Sur ssd detached in the past hours 5.8 is working fine again no simple to debug where is my problem but for now it is working well1 point
-
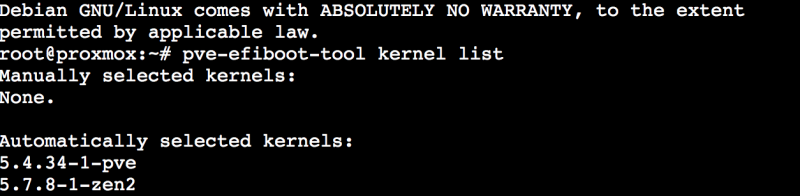
@meina222usually I copy new kernel deb files in proxmox root then from shell I execute command to install dkpg -I *.deb i have different kernel installed from 5.34 because it is an old proxmox installation1 point
-
1 point
-
@meina222do not worry I appreciate your work and if I was so safe with my rig..we have not a public solution for trx40 and OSX 🙂 Again thank you for your kernel I have few skill to understand where my system now is failing with it1 point
-
Beta 4 is here. I have also installed Nvidia driver (patched) to have dual display and a minimal functionality on display graphics as I have had in Mojave or in Catalina Installation notes Same open core 060 latest release debug version with all kext and drivers updated During first installation step I have used old Penryn args for VM config1 point
-
Post your vfio.conf also lspci -nnk but i think if you followed pavos github you block things he is blocking because he starts or started in the past his guest from web interface on another pc i can be wrong...1 point
-
remove it from vfio.conf also you can try to unblacklist amdgpu from blacklist.conf in my rig I do not use any block and it works1 point
-
1 point
-
1 point
-
Thank you and don't worry risk is mine 🙂 I will try ands see if it boots1 point
-
1 point
-
1 point
-
About opencore we are talking about 060 release in Italian forum section i have installed o60 release debug version with no problem at all1 point
-
If I have understood well it is possible to use if you do not use zfs..and so..is it available a compiled kernel in this way? I would like to test if it adds some opportunity to pass bridge or pcieport.. I think it is a qemu problem than kernel..but I am not sure of this my assertion 🙂1 point
-
and also for me is not useful to block all that stuff in blacklist.conf and in vfio.conf but I can't say for sure because many of you and Proxmoxwiki advice to do that... maybe I am lucky 🙂1 point
-
@tsongz are you sure you need all those ssdt to have cpu as host booting fine? In my MSI board no need for any of these ssdt, only to configure vm config and config.plist in open core properly (for owned hardware I mean)1 point
-
Misunderstood clarified! 🙂 I took it a bit since in December 2019 (on December 6 amazon gave me the cpu) I started thinking about finding a way to make this system work under osx The community said it should have worked with old patches I made myself available to Algrey to perfect all the tests he wanted to do, also buying serial cards to make a serial output of the problem and often taking fish in the face from other users who said that I was not able to do a serial output and to send a trx40 chip to the developers I lost hope when Algrey also told me to think about linux, which was perhaps the best solution I tried the road with the OpenCore developers, who, with difficulty, gave me some steps to do, and with these we understood that the problem was patches (which they called "borked" This is to tell you that during this process of knowledge I caught several fish in the face (Italian idiom) but I went ahead managing to have already since January the first hack made with TRX40 perfectly functional and performing then I decided to write this guide (you can find it in guides) which is not perfect, but it is certainly the most detailed and free that you can find around today happy with the clarification you had, when possible it would be useful to see how your frontier performs, perhaps with the test on davinci resolve, cinebench 15 and with luxmark3.1 Thanks and welcome again 🙂1 point
-
to have a dedicated thread for our experimental TB3 support I have created a new thread where we can write and discuss about this subject Thank you your partecipation1 point
-
mine: @meina222 if you have time post also Cinebench 20 results thank you1 point
-
@Rox67erto pass your sata controllers there is some trick to know? if you have all nvme controller used I mean asrock trx40 creator share those controllers in some way? @Driftwood what did you do to pass it?1 point
-
maybe you have to take a look here (You AMD Navi GPU owner I mean 🙂 ) I have asked to include Navi patch on zen2 kernel 🙂 https://github.com/fabianishere/pve-edge-kernel/issues/51 point
-
1 point